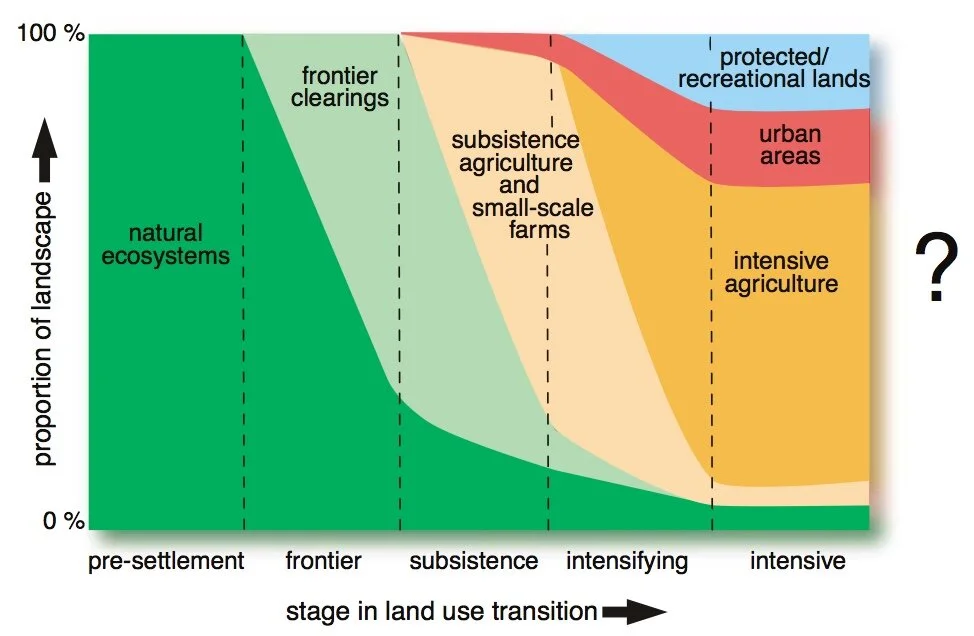
Defining the American urban form relies on a perceived division between ‘urban’ and ‘rural’ areas. I trace the idea of the urban/rural divide through the evolution of human settlement patterns in the United States from the nineteenth century onwards. I argue that while a superficial distinction between urban and rural land was once relevant to characterizing city forms and metropolitan growth trends, in contemporary contexts there no longer exists an actual separation of lands based on their ‘natural’ character around cities. Thus, continuing to plan for urban/rural areas ignores how pressing planning concerns arise from greater socio-ecological processes, and places that extend beyond designated settlement boundaries. I explore how new conceptualizations of urbanization, including urban sustainability, urban resilience, and planetary urbanization, can inform a post-urban/rural divide planning paradigm.
“Seeing from the South” (Watson 2008) and “Re-engaging Planning Theory with South-Eastern Perspectives” (Yiftachel 2006) are essential calls for the development of planning theories and empirical research from the Global South. Such scholarship has interpreted the rationalities at play as informal settlements develop on the peripheries of rapidly globalizing cities and explored how they reflect the nature of state interventions. This article examines the utility of planning theories issued from the Global South and North in explaining a case of state planning for an indigenous, ethnic minority in Israel: the Negev/Naqab Arab-Bedouins. The researchers conducted 90 interviews with planners, engineers, Bedouin residents, government officials, academics, and employees of non-governmental organizations. Their aim was to understand how stakeholders comprehended, engaged with, and approached planning for the Abu-Basma Regional Council, a state initiative to plan and provide services to informal Bedouin villages in Israel’s south, as well as the program’s outcomes. The findings indicate that planning theories from the Global South, which are focused on space, resource distribution, and resident-driven spatial change, are essential to understanding the outcomes of planning. They provide a necessary context for the North’s normative/prescriptive planning theories, which highlight tangible “episodes” (Healey 2007, 78) of planning practice but risk misattributing popular resistance to a program’s communication challenges, rather than to residents’ fundamental objections.
The urban and rural co-dependency in Lebanon has been drastically transformed and further heightened since the joining of both territories with the Declaration of Greater Lebanon on September 1st, 1920. The lack of any formal planning during the past century has driven socio-political and economic forces to shape or disfigure the built environment. Historians, geographers, and urban planners have addressed Lebanon’s urban-rural divide by highlighting unequal development. Even still, a comprehensive overview of key historical moments that investigates migrations and the economic system is needed to understand the current co-dependent and conflicted relationship between both territories. Accordingly, this paper explores the urban and rural dynamics starting from the early nineteenth century to modern- day Lebanon, by juxtaposing the flow of migrations between Mount Lebanon and Beirut with the country’s neoliberal economic policies. This analysis is derived from historical books, articles, and theses on the region and aims to highlight the integration of the rural feudalist- sectarian structure with the hyper-financialized urban neoliberal system.
The conceptual dyad of urban/rural has long formed the basis of the planner’s description of space. However, the terms themselves are increasingly insufficient to describe the world in which we live, presenting as overdetermined and reductive signifiers. In this photographic essay, we use Google Earth satellite images to examine a series of locations where descriptors such as ‘urban’ and ‘rural’ falter against manifold, shifting, and unstable landscape forms. We draw on Henri Lefebvre’s concept of the abstract spaces of capitalism, globalization, and urbanization, which he argued are dialectically produced through their interaction with landscape. However, where Lefebvre contended that abstraction instantiates in more or less discrete typological forms, we argue that abstract space only becomes intelligible under conditions of ‘entanglement,’ where qualities such as ‘urban’ and ‘rural’ become momentarily comprehensible at the instant we observe or describe them. In the end, holding the world still long enough to describe it reveals crucial patterns and relations, but always at a cost, always with the risk of reduction, simplification, and overdetermination. Such pitfalls are inevitable in research; however, they become all the more prevalent as the terms we use to describe the world become less and less applicable, and as the accumulation of anomalies compels us to build new models and to tell new stories.
Capitalist agriculture faces a crisis. Plateauing yields and profits are driving up food prices, and the ability to continue the traditional practice of expanding into new, un-commodified territories appears to be waning. This crisis is due in large part to the accelerating biophysical contradictions of industrial agriculture, which systematically undermine the ecological conditions for its own success in pursuit of profit. We investigate how digital technologies are deployed as a potential data fix that does not solve the crisis but merely staves it off. We situate these technologies within the material context of capitalist urbanization, along the way arguing for bringing information back into the neo-Lefebvrian framework of “extended” or “planetary” urbanization. Digital agriculture technologies continue the centralization of economic knowledge and power as they facilitate the transformation of vast territories into “operational landscapes” that provide the material, energy, and labor for a rapidly expanding urban system.